Common Casting Defects and their solutions
Casting Defects: Causes, Types, and Ways to Prevent Them
 |
| Tanveer Engineering |
Introduction
Casting is an old and common way to make metal parts. Even with new tech, flaws still happen. These flaws hurt the quality and cost of metal parts. Knowing about these flaws helps cut waste in metal shops.
This article looks at why flaws matter. It also covers flaw types, causes, and fixes for the metal industry.
- What Are Casting Defects and Why Are They Important?
Casting defects are flaws in the metal part. These flaws hurt the final product. Flaws can make parts:
- Weak
- Less durable
- Wasteful
- Costly to fix
Shops must find and fix flaws. This improves quality and saves money.
- Types of Casting Defects
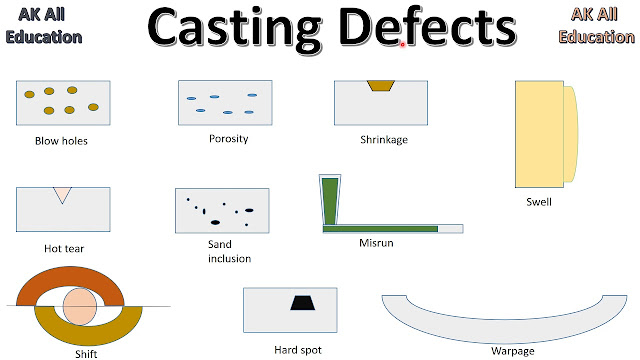
Flaws fall into types like porosity, shrinkage, and surface issues.
a. Porosity Defects
Porosity means small holes inside the metal. These holes weaken the part.
Common porosity flaws:
- Gas Porosity: Gas trapped as the metal cools.
- Pinholes: Tiny holes from gas in the hot metal.
- Blowholes: Big gas pockets on the part's surface or inside.
b. Shrinkage Defects
Shrinkage flaws happen as metal shrinks when it cools. This makes holes or cracks.
Types of shrinkage flaws:
- Macro Shrinkage: Big holes you can see.
- Micro Shrinkage: Tiny holes that make the metal weak.
- C Surface Defects
Surface defects impact how a casting looks and works. Common issues include cold shuts where metal doesn't fully fuse, creating weak spots. Misruns occur when the mold isn't completely filled. Scabs are rough areas from sand mold damage.
d Dimensional Defects
Dimensional defects mean the casting's size is wrong. Warpage happens when uneven cooling bends the metal. Mold shift causes misalignment, making the casting off-center.
3 Causes of Casting Defects
Many things cause casting defects.
a Material issues include metal impurities or the wrong mix. Too much moisture in the sand is also a problem.
b Processing issues include bad gate and riser designs. Incorrect pouring heat and poor venting cause defects too. Vents release trapped gasses.
c. Design flaws are also a cause. Sharp corners and big changes in thickness are bad. Not enough draft angles and poor mold design lead to uneven cooling.
 |
| Tanveer Engineering |
4. Preventing defects needs good materials, process control, and checks.
a. Use quality metal alloys to avoid impurities. Use the right sand to prevent moisture issues.
b.Keep the pouring heat and speed correct. Good gating and riser systems help metal flow smoothly. Use proper venting to release gasses.
c Make sure thickness is even to stop shrinking. Use fillets to round sharp corners. Align the mold to avoid shifts and warpage.
d. Check castings with methods like X-rays and ultrasound. Use CAD to design better molds. Keep molds in good shape with regular checks.
- Modern Research and Tech Cut Down on Flaws
Tech gains have greatly cut flaws in casting. This comes from better control and machines.
a. Simulation Tools
Software like MAGMASOFT helps find flaws early. This lowers the cost of fixing problems.
b. AI
AI helps find problems and fix machines. This lets makers fix issues before flaws appear.
c. 3D Printing
3D printing changes mold-making. It makes molds exact and cuts down on mistakes.
d. Better Testing
X-rays find flaws inside without damage. Lasers check sizes to make sure castings are right.
Conclusion
Flaws still cause problems in metal work. But makers can lower these with new tech and better ways. By knowing what causes flaws and how to stop them, the field can work better. It can also waste less and make better products.


Comments
Post a Comment